- Windows Docker Run Linux Container List
- Windows 2016 Docker Run Linux Container
- Windows Server Docker Run Linux Container
- Windows Server 2019 Docker Run Linux Container
- Run Docker Linux Container On Windows
Docker Desktop networking can work when attached to a VPN. To do this, Docker Desktop intercepts traffic from the containers and injects it into Windows as if it originated from the Docker application. When you run a container with the -p argument, for example.

Windows Docker Run Linux Container List
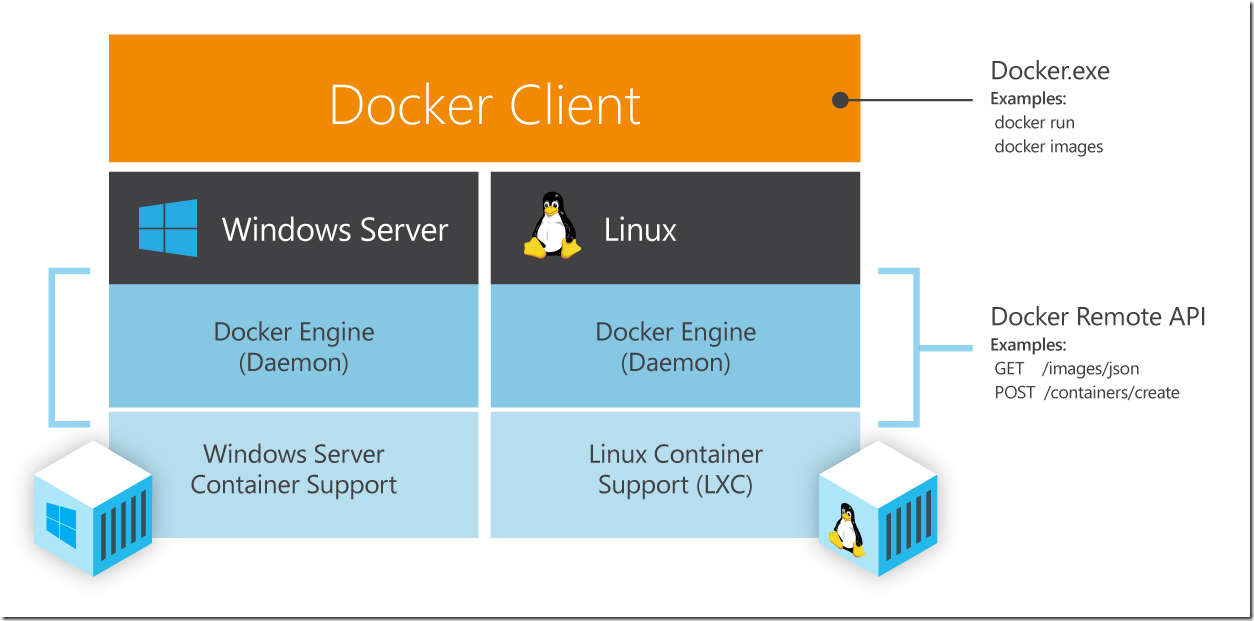
- Docker for Windows can run Linux or Windows containers, with support for Linux containers via a Hyper-V Moby Linux VM (as of Docker for Windows 17.10 this VM is based on LinuxKit). The setup for running Linux containers with LCOW is a lot simpler than the previous architecture where a Hyper-V Linux VM runs a Linux Docker daemon, along with all.
- Running Docker Linux containers on Windows requires a minimal Linux kernel and userland to host the container processes. This is exactly what the LinuxKit toolkit was designed for: creating secure, lean and portable Linux subsystems that can provide Linux container functionality as a component of a container platform.
Windows 2016 Docker Run Linux Container
This topic describes how to run your first Windows container, after setting up your environment as described in Get started: Prep Windows for containers. To run a container, you first install a base image, which provides a foundational layer of operating system services to your container. Then you create and run a container image, which is based upon the base image. For details, read on.
Install a container base image
All containers are created from container images. Microsoft offers several starter images, called base images, to choose from (for more details, see Container base images). This procedures pulls (downloads and installs) the lightweight Nano Server base image.
Open a command prompt window (such as the built-in command prompt, PowerShell, or Windows Terminal), and then run the following command to download and install the base image:
Tip
If you see an error message that says
no matching manifest for unknown in the manifest list entries, make sure Docker isn't configured to run Linux containers.After the image is finished downloading—read the EULA while you wait—verify its existence on your system by querying your local docker image repository. Running the command
docker imagesreturns a list of installed images.Here's an example of the output showing the Nano Server image.

Run a Windows container
For this simple example, a ‘Hello World’ container image will be created and deployed. For the best experience, run these commands in an elevated command prompt window (but don't use the Windows PowerShell ISE—it doesn't work for interactive sessions with containers, as the containers appear to hang).
Start a container with an interactive session from the
nanoserverimage by entering the following command in your command prompt window:After the container is started, the command prompt window changes context to the container. Inside the container, we'll create a simple ‘Hello World’ text file and then exit the container by entering the following commands:
Get the container ID for the container you just exited by running the docker ps command:
Create a new ‘HelloWorld’ image that includes the changes in the first container you ran. To do so, run the docker commit command, replacing
<containerid>with the ID of your container:When completed, you now have a custom image that contains the hello world script. This can be seen with the docker images command.
Here's an example of the output:
Finally, run the new container by using the docker run command with the
--rmparameter that automatically removes the container once the command line (cmd.exe) stops.The result is that Docker created a container from the 'HelloWorld' image, Docker started an instance of cmd.exe in the container, and the cmd.exe read our file and output the contents to the shell. As the final step, Docker stopped and removed the container.
Run a Windows container using Windows Admin Center
Windows Admin Center can be used to run your containers locally. Specifically, you use the the Containers extension of your Windows Admin Center instance to run the containers. First, open the container host you want to manage, and in the Tools pane, select the Containers extension. Then, select the Images tab inside the Container extension under Container Host.
Windows Server Docker Run Linux Container
If your host doesn't have a base container image, select the Pull option which opens the following:
Windows Server 2019 Docker Run Linux Container
In the Pull Container Image settings, provide the image URL and the tag. If you aren't certain which image to pull, Windows Admin Center provides a list of common images from Microsoft. You can also provide the credentials to pull an image from a private repository. Once you fill out the necessary information, click Pull. Windows Admin Center will start the pull process on the container host. After the download is complete, you should see the new image on the Images tab.
Select the image you want to run, and click Run.
On the Run menu, set up the configuration for the container, such as the container name, the isolation type, which ports to publish, and memory and CPU allocation. Additionally, you can append Docker run commands that are not in the UI, such as -v for persistent volume. For more information on available Docker run parameters, review the documentation.
Run Docker Linux Container On Windows
Once you have finished the configuration for the container, click Run. You can see the status of the running containers on the Containers tab:
Next steps
